
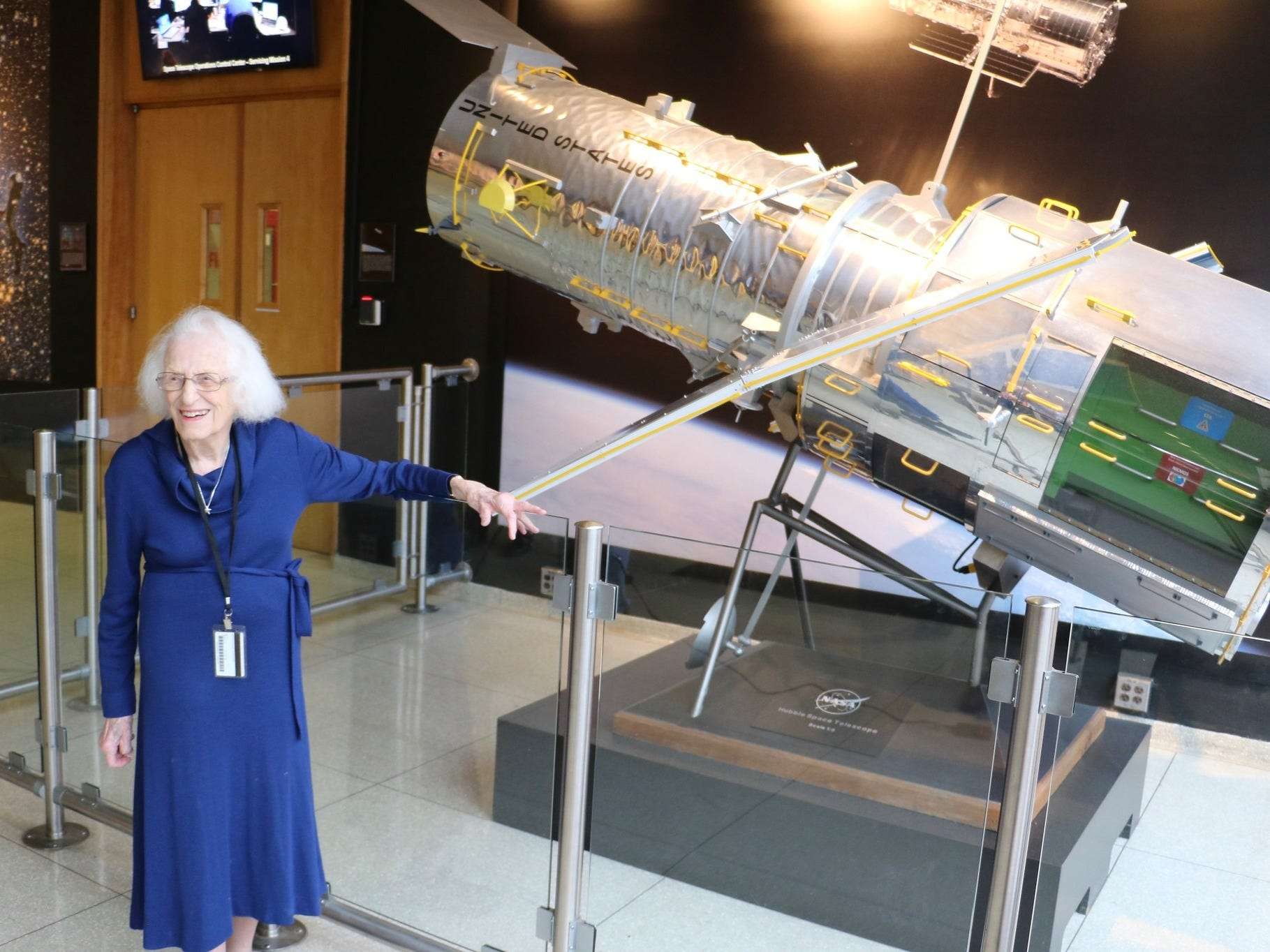
Picture : Nancy Grace Roman stands in front of a scale model of the Hubble Space Telescope. She was an advocate for "Women in the Sciences". She was a pioneer in astronomy, earning her doctorate and conducting early research to map the Milky Way galaxy in the 1950s. She created NASA's space astronomy program and is known to many as the "Mother of Hubble" for her foundational role in planning the Hubble Space Telescope. Roman served as NASA's first Chief of Astronomy throughout the 1960s and 1970s. Both the telescope and its namesake are powerhouses in their own right.ĭr. The Roman space telescope, launching in 2026, is named after NASA's first female executive, Dr. Nancy Grace Roman's legacy today for Women's History Month. Seeing the universe in its early stages will help unravel how it has expanded throughout its history, which will hint at how it may continue to evolve.🎉 We are celebrating Dr.

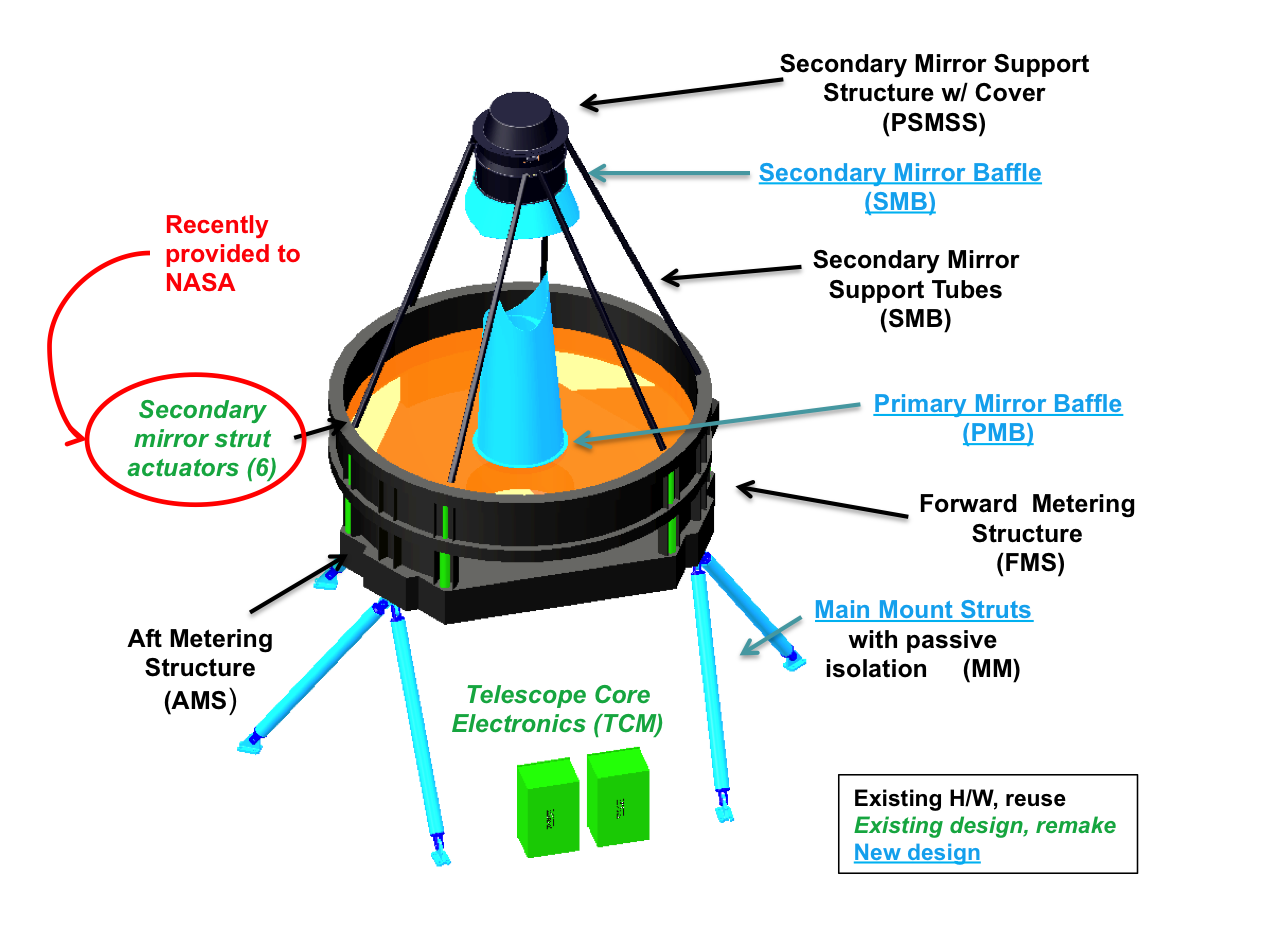
The Wide Field Instrument is a 300-megapixel infrared camera that will allow scientists to look very far back in time. The primary mirror, in concert with other optics, will send light to Roman’s two science instruments – the Wide Field Instrument and Coronagraph. Roman’s mirror weighs only 410 pounds (186 kilograms) thanks to major improvements in technology. The assembly will help Roman solve some of the most profound mysteries in astrophysics. While it’s the same size as the Hubble Space Telescope’s main mirror, it is less than one-fourth the weight. Engineers at Ball Aerospace, one of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescopes industrial partners, have installed and aligned the element wheel assembly into the observatory’s Wide Field Instrument. Roman’s primary mirror is 7.9 feet (2.4 meters) across. The amount of detail these observations will reveal is directly related to the size of the telescope’s mirror, since a larger surface gathers more light. The thermal stability of an observatory at L2 will provide a ten-fold improvement beyond Hubble in much of the data Roman will gather. Roman’s barrel-like shape will help block out unwanted light from the Sun, Earth, and Moon, and the spacecraft’s distant location will help keep the instruments cool. NASA’s Roman Space Telescope to Uncover Echoes of the Universe’s Creation released on Nov 18 Press release from STScI Roman Space Telescope Could Image 100 Hubble Ultra Deep Fields at Once on Jan 11 NASA’s Roman Mission Will Probe Galaxy’s Core for Hot Jupiters, Brown Dwarfs released on Jan 25.

At this special place in space, called the second Sun-Earth Lagrange point, or L2, gravitational forces balance to keep objects in steady orbits with very little assistance. To make Roman’s sensitive measurements possible, the telescope will observe from a vantage point about 930,000 miles (1.5 million km) away from Earth in the direction opposite the Sun. The mission will help us solve some of the most profound mysteries in astrophysics, such as how the universe has evolved, its ultimate fate, and whether we are alone. The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is a next-generation observatory that will peer through dust and across vast stretches of space and time to survey the infrared universe.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
